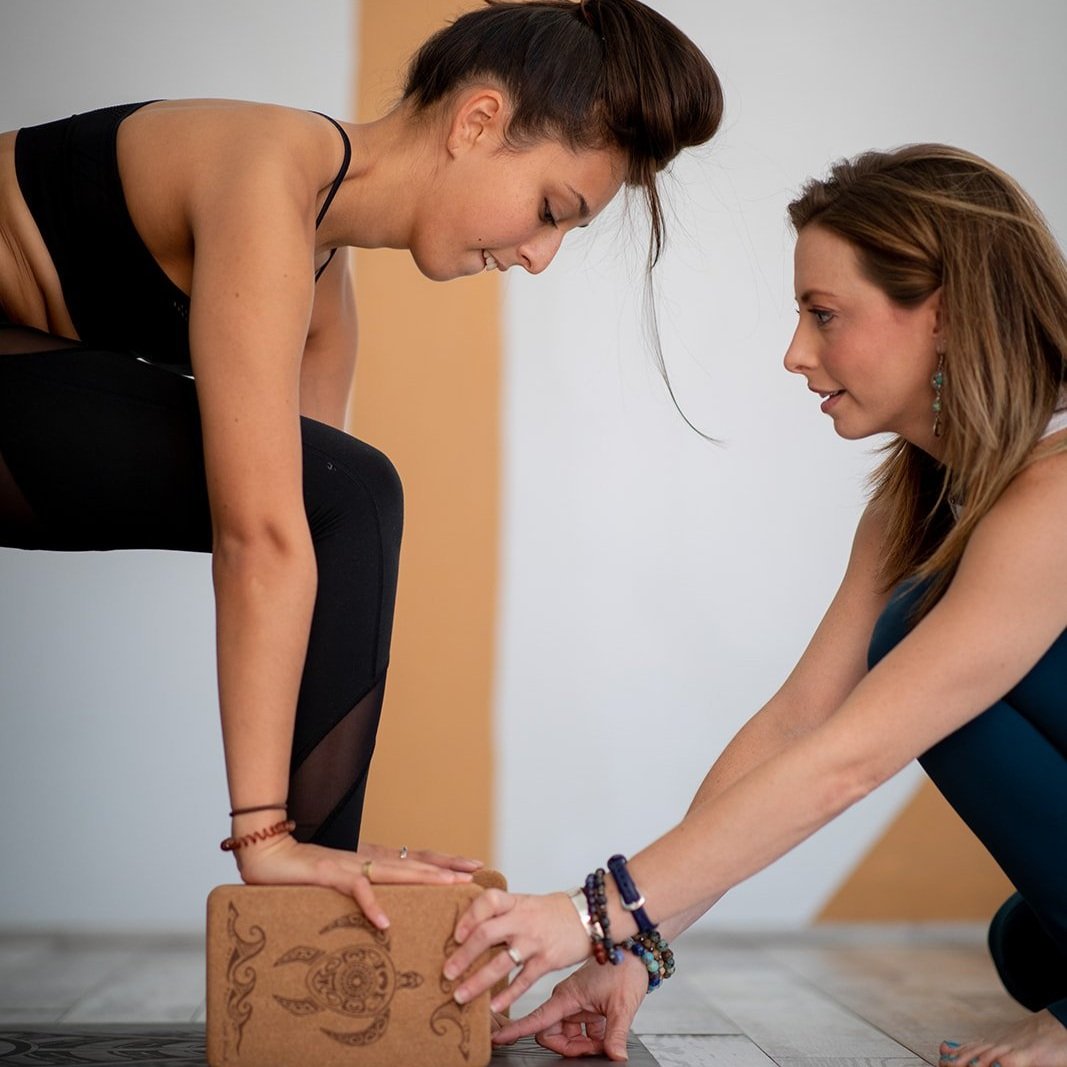
What is Yoga Therapy?
Evidence-Based Holistic Health. Personalized for YOU.
Yoga Therapy (“Yoga Chikitsa”) is a holistic healing art that focuses on the treatment and healing of the whole person to achieve optimal health, healing, and well-being. As an evidence-based practice that is supported through both modern clinical research and thousands of years of historical application, Yoga Therapy comes alongside conventional medical therapies and treatments to carefully, safely, and effectively address the suffering, disease, and dis-ease that may arise within any and all domains of the individual experience.
Supported by a growing body of modern medical research for its safety, efficacy, and accessibility, Yoga Therapy involves the professional adaptation and application of Yogic and Ayurvedic principles, practices, and techniques (including movement, beathwork, meditation, relaxation, and lifestyle intervention) to address and ameliorate individual challenges to physical, psychological, emotional, and spiritual health. Yoga Therapy helps individuals better manage their condition, reduce symptoms, restore balance, increase vitality, and improve overall outcomes and well-being. Through its holistic, whole-person approach, Yoga Therapy gently invites presence, awareness, and intuition into the healing journey, helping patients establish a more compassionate, loving, and non-judgmental relationship to their individual health, well-being, and healing process.
Within the therapeutic relationship between a professional Yoga Therapist and their patient, treatment is personalized, collaborative, and regularly re-assessed so as to best support the specific needs, goals, and progress of the patient and their condition(s). Yoga Therapy treatment includes personalized assessment, goal setting, lifestyle management, and individualized practices that progressively and intuitively aid the patient in achieving their particular physical, psychological, spiritual, or physiological goal(s). Yoga therapy is inclusive and accessible, respecting individual differences in age, culture, religion, philosophy, occupation, and mental and physical health, and is continually applied with great care and intention to best meet the patient where they are, as they are.
What Conditions Does Yoga Therapy Help?
While acute diseases and conditions fall outside the scope of practice of the Yoga Therapist (such as recent injuries and illnesses), Yoga Therapy is hugely beneficial for the treatment and management of chronic conditions, rehabilitation after the acute phase of injury or illness, and long-term prevention and mitigation of health challenges.
Yoga Therapists do not diagnose, but rather, work integratively and collaboratively with the entire clinical care team to best support the patient on their healing journey.
Yoga Therapy can be beneficial for a wide array of health challenges and conditions, including but not limited to:
-
Chronic pain affects millions of individuals, often leading to significant disruptions in daily life and overall well-being. It is defined as pain that lasts longer than three months, often persisting beyond the typical recovery period of an injury. This condition can arise from a variety of sources, including but not limited to previous injuries, medical conditions like arthritis or fibromyalgia, and even stress or psychological factors.
Yoga can be an effective practice for managing chronic pain. Incorporating gentle movements, breath awareness, and mindfulness, yoga helps to alleviate discomfort and improve overall well-being. Here are some key benefits and considerations for practicing yoga if you experience chronic pain:
Benefits of Yoga for Chronic Pain
Increases Flexibility: Gentle stretches can help improve range of motion, which may reduce stiffness and discomfort associated with chronic pain.
Enhances Strength: Yoga poses build strength in key muscle groups, providing better support for the body and potentially easing the strain on affected areas.
Promotes Relaxation: Breathing techniques and meditation foster a sense of calm and can decrease stress, which often exacerbates the perception of pain.
Improves Posture: Many chronic pain conditions are worsened by poor posture. Yoga encourages awareness of body alignment, which can lead to better posture and reduced pain.
Encourages Mindfulness: By focusing on the present moment, yoga can help shift the focus away from pain, fostering a more positive relationship with your body.
Incorporating yoga into your routine can provide relief from chronic pain, as well as enhance your overall sense of well-being.
-
Low back pain is a common condition that affects many individuals at some point in their lives. It can stem from various causes, including muscle strain, poor posture, herniated discs, or underlying health issues. Understanding and addressing low back pain through preventive measures and management strategies such as Yoga and mindfulness can lead to better overall well-being and a more active lifestyle.
Sciatica is characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks down to each leg. This condition typically occurs when the nerve is compressed, often due to a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or bone spur on the spine. While sciatica can result from specific injuries, it’s often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor posture, prolonged sitting, or lack of physical activity.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for alleviating some of the discomfort associated with low back pain and sciatica by promoting flexibility, strengthening the muscles around the spine, and enhancing overall body awareness.
-
Heart disease and hypertension are significant health concerns that affect millions of individuals worldwide. Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that affect the heart's structure and function, including coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems, and heart defects. Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is often a major contributing factor to heart disease and can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Yoga can be an effective complementary approach for managing hypertension. Through a combination of physical postures, breath control, and meditation, yoga helps reduce stress, improve circulation, and promote overall well-being, which can be beneficial for those with high blood pressure. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Benefits of Yoga for Hypertension
Stress Reduction: Stress is a significant contributor to high blood pressure. Yoga practices, particularly those that emphasize relaxation and mindfulness, can lower stress levels and create a sense of calm.
Enhanced Circulation: Specific poses can enhance blood flow and improve cardiovascular health. Poses that involve gentle stretching can help open up the blood vessels.
Breath Control: Pranayama, or breath control, is an essential element of yoga that aids in relaxation and can lower heart rate and blood pressure. Techniques such as deep breathing and alternate nostril breathing are particularly beneficial.
Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices promote mental clarity and emotional stability, which can lead to reduced anxiety and lowered blood pressure over time.
Incorporating yoga into your routine may support lower blood pressure and improve overall health. Consistent practice, combined with other healthy lifestyle changes, can enhance its effectiveness. Remember to approach your practice with mindfulness and patience, allowing yourself to experience the benefits over time.
-
Migraine headaches are a common neurological condition characterized by intense, debilitating pain often accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. These headaches typically affect one side of the head but may also occur on both sides. Migraine headaches can significantly impact daily life, but understanding triggers and effective management strategies can lead to improved quality of life.
Incorporating yoga into your routine may help alleviate some symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. Yoga can serve as a complementary practice in managing migraines, promoting relaxation, and reducing stress. Regular practice, combined with other treatment options, may lead to improved well-being.
-
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. This condition can lead to feelings of fatigue, irritability, and difficulties concentrating throughout the day. While occasional sleeplessness is normal, chronic insomnia can significantly impact overall well-being. Managing insomnia is essential for overall health and well-being. Through understanding its causes and implementing effective strategies, individuals can work towards achieving more restful and restorative sleep.
Yoga has been shown to improve sleep quality through various mechanisms. First, practicing yoga helps to reduce stress and anxiety, which are common barriers to restful sleep. The physical postures, or asanas, encourage relaxation and help to release tension in the muscles, preparing the body for sleep.
The emphasis on breath control, or pranayama, in yoga promotes a calm mind and supports emotional regulation. By focusing on deep, controlled breathing, practitioners can activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which counteracts the effects of stress and induces a state of relaxation.
Regular yoga practice can also enhance the body’s overall balance and promote better sleep hygiene. Specific poses, such as forward bends and restorative postures, facilitate gentle stretching that improves circulation and reduces discomfort, making it easier to fall asleep.
Moreover, yoga encourages mindfulness and self-awareness. By creating a greater connection to the body and its needs, individuals can develop healthier routines and habits that contribute to improved sleep patterns. Engaging in a mindful practice before bedtime can signal to the body that it's time to wind down, establishing a consistent pre-sleep ritual.
In summary, the combination of physical relaxation, breath control, stress reduction, and enhanced mindfulness makes yoga an effective tool for improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
-
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body processes glucose, a type of sugar. There are two primary types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, which occurs when the body does not produce insulin, and Type 2 diabetes, which occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn't produce enough. Managing diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach that often includes dietary changes, regular physical activity, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and, in some cases, medication or insulin therapy.
Yoga can be a valuable addition to diabetes management, offering both physical and mental health benefits. Engaging in regular yoga practice can help regulate blood sugar levels, enhance insulin sensitivity, and reduce stress, which is crucial for those managing diabetes.
Benefits of Yoga for Diabetes Management
Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Yoga may enhance the body's ability to use insulin effectively, contributing to better blood glucose control.
Reduces Stress: Mindfulness and relaxation practices in yoga can lower cortisol levels, potentially stabilizing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes complications.
Promotes Physical Activity: Regular yoga session encourages movement, which can aid in weight management and improve overall physical fitness.
Enhances Circulation: Certain yoga poses promote better blood flow, which is essential for overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes.
Encourages Mindful Eating: Yoga fosters awareness and mindfulness, facilitating healthier eating habits that support blood sugar management.
Incorporating yoga into a comprehensive diabetes management plan can lead to improved physical health and emotional well-being. Consistency, alongside a balanced diet and regular medical care, can contribute to better health outcomes for those managing diabetes.
-
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS), often referred to as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME/CFS), is a complex disorder characterized by profound fatigue that lasts for six months or longer and is not improved by rest. This condition can significantly impair daily functioning and quality of life. The fatigue experienced is often accompanied by a range of other symptoms, which can be variable and sometimes debilitating. The experience of CFS can vary significantly among individuals, with some people facing severe limitations while others may only experience intermittent symptoms. Diagnosing CFS can be challenging, as there is no specific test to confirm the condition. Physicians typically rely on a detailed medical history and symptom evaluation, often ruling out other potential causes of fatigue through various tests.
Yoga can serve as a complementary method to help manage CFS symptoms and improve overall well-being. Benefits of Yoga for CFS include:
Gentle Movement: Yoga offers low-impact movement that can help maintain flexibility and strength without overexertion. This is particularly important for those with CFS, as high-intensity workouts can lead to increased fatigue.
Stress Reduction: The mindfulness aspects of yoga, which include breathwork and meditation, can help alleviate stress and anxiety, potentially reducing the psychological burden associated with CFS.
Improved Sleep: Certain yoga practices may promote better sleep hygiene, helping to address one of the common challenges faced by those with CFS. A calming evening routine that includes gentle yoga can signal the body to wind down.
Enhanced Body Awareness: Practicing yoga encourages a deeper connection with one's body and its needs. This heightened awareness can lead to better pacing and management of energy levels throughout the day.
Incorporating yoga into the routine for managing Chronic Fatigue Syndrome can provide a supportive framework for improving physical and mental well-being.
-
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. It affects how the brain processes pain signals, leading to heightened sensations of discomfort. The exact cause of fibromyalgia is not fully understood, but factors such as genetics, infections, physical or emotional trauma may contribute to its development. Diagnosis is primarily based on patient-reported symptoms and exclusion of other conditions, as no definitive tests exist. While fibromyalgia is a chronic condition with no known cure, understanding it better and adopting effective management strategies can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Incorporating yoga into your routine can be beneficial for managing these symptoms and improving overall well-being. Pranayama (breath control) exercises can be incredibly beneficial for fibromyalgia; The focus on deep, diaphragmatic breathing helps to reduce stress and promote relaxation, and practicing mindfulness can help manage the emotional aspects of fibromyalgia.
-
Prenatal yoga offers a safe and supportive environment for expectant mothers to connect with their bodies and their growing babies. This practice focuses on gentle poses that promote flexibility, strength, and relaxation. Postpartum yoga focuses on helping new mothers recover physically and emotionally after childbirth. This practice emphasizes gentle movements that encourage healing, restore energy, and promote connection with the baby. Both prenatal and postpartum yoga provide essential support during the transformative journey of motherhood. By fostering physical strength, emotional stability, and community connection, these practices contribute to overall well-being for mothers and their babies.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects people with ovaries, often during their reproductive years. It is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen levels, and polycystic ovaries. While the exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Managing PCOS often requires a holistic approach that includes lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise, medical treatment, and support for mental health. Regular physical activity is also crucial in improving metabolic health and hormonal balance. Emotional well-being is an essential aspect of living with PCOS. Many experience stress, anxiety, or depression related to their symptoms and challenges with fertility. Support groups, counseling, and mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, can be valuable tools in navigating these emotional landscapes.
PCOS is a complex condition that varies from person to person. Individualized treatment plans and ongoing communication with healthcare providers can help those with PCOS manage their symptoms effectively and improve their overall quality of life.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for managing some of these symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Benefits of Yoga for PCOS
Stress Reduction: Yoga promotes relaxation through deep breathing and meditation practices, which can help lower cortisol levels. High cortisol may contribute to weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
Hormonal Balance: Certain yoga poses may stimulate the endocrine system, helping to regulate hormone levels. Poses like the bridge pose, shoulder stand, and fish pose are particularly beneficial.
Weight Management: Regular yoga practice can aid in maintaining a healthy weight. Flow-based or dynamic styles of yoga, like Vinyasa or Ashtanga, can provide a cardiovascular workout, which is essential for weight management.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Some studies suggest that yoga can improve insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for women with PCOS. Poses that encourage digestion and abdominal strengthening may support metabolic health.
Enhanced Mood: The mindfulness practices inherent in yoga can lead to improved mental well-being, reducing anxiety and depressive symptoms often associated with PCOS.
Yoga can be a valuable part of a comprehensive approach to managing the condition. By integrating yoga into your routine, you can cultivate greater balance in both body and mind.
-
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. It can originate in almost any tissue and may spread to other parts through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. There are over 100 different types of cancer, classified primarily by the type of tissue involved, including carcinoma, sarcoma, leukemia, lymphoma, and central nervous system cancers. The development of cancer is usually attributed to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Symptoms can vary widely, often depending on the type of cancer and its location. Early detection through screening and awareness is crucial, as it can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
Supportive care, including psychological support and complementary therapies like yoga and mindfulness, plays an essential role in the overall well-being of patients. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, can help reduce the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Yoga can be a supportive practice for individuals diagnosed with cancer, helping to foster both physical and emotional well-being during treatment. Research indicates that incorporating yoga can lead to reduced symptoms of anxiety, depression, and fatigue, while also enhancing overall quality of life.
Benefits of Yoga for Cancer Patients
Physical Strength and Flexibility: Gentle yoga postures promote strength and flexibility, which may be beneficial, especially after surgery or during treatment. This practice can help maintain or improve mobility.
Stress Reduction: Mindfulness and breathing techniques in yoga can aid in reducing stress and promoting relaxation, creating a sense of calm during uncertain times.
Pain Management: Certain yoga practices may assist in managing pain associated with cancer treatments or symptoms, encouraging a more comfortable state of being.
Community Support: Participating in yoga classes designed for cancer patients can foster a sense of community and connection with others facing similar challenges.
Enhancing Sleep: Incorporating gentle yoga routines can improve sleep quality, which is essential for recovery and overall health.
In summary, yoga can serve as a valuable adjunct to cancer treatment, offering numerous benefits that support physical health and emotional resilience. By approaching the practice mindfully, individuals can find strength, peace, and connection on their journey.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) encompasses a group of chronic inflammatory conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, primarily including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions are characterized by periods of flare-ups and remission, leading to various symptoms that can significantly impact quality of life. The exact cause of IBD remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Treatment options for IBD aim to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and maintain remission. Living with IBD requires ongoing management and support.
Yoga can be a valuable practice for individuals living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes conditions like Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. It can complement traditional therapies and contribute to overall well-being, help alleviate stress, and improve gastrointestinal function.
Benefits of Yoga for IBD
Stress Reduction: Stress can exacerbate IBD symptoms. Yoga promotes relaxation and helps to lower stress levels through deep breathing, meditation, and gentle movement.
Improved Digestion: Certain yoga poses can stimulate digestion and promote gastrointestinal health. Poses that involve gentle twists may help massage the intestines and encourage healthy bowel function.
Increased Flexibility and Strength: Regular practice can improve overall physical fitness, increasing flexibility and strength, which may enhance mobility and function.
Mind-Body Connection: Yoga fosters mindfulness, helping individuals manage their symptoms and improve their emotional well-being. This can lead to better coping strategies during flare-ups.
Integrating yoga into your routine may enhance your quality of life and provide supportive benefits associated with managing inflammatory bowel disease.
-
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, tissues, or organs. This misdirected response can lead to inflammation, damage, and dysfunction in various parts of the body. There are over 80 known autoimmune diseases, each with distinct symptoms and impacts, making diagnosis and treatment complex. Treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms and suppressing the immune system's abnormal response.
A holistic approach to managing autoimmune disorders can enhance overall well-being. Integrating therapies such as yoga can promote flexibility, reduce stress, and improve mental health. Mindfulness practices may also support emotional resilience, helping individuals navigate the challenges posed by these conditions.
Yoga can serve as a beneficial practice for individuals with autoimmune disorders, providing both physical and emotional support. The gentle nature of yoga allows for modifications, making it accessible to various levels of ability and energy. Here are several ways yoga can aid those with autoimmune conditions:
1. Reducing Inflammation
Certain yoga practices focus on mindful movement and breath control, which can help reduce inflammation in the body. Gentle stretching and restorative poses may foster circulation and promote overall health.
2. Enhancing Flexibility and Strength
Regular yoga practice can improve flexibility and build strength, which is often compromised by autoimmune disorders. Strengthening muscles and maintaining joint mobility can ease some physical discomfort and improve daily functioning.
3. Managing Stress
Stress can exacerbate autoimmune symptoms. Yoga encourages relaxation through techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness. Engaging in these practices can help mitigate stress, promoting emotional well-being.
4. Improving Sleep Quality
Sleep disturbances are common in those with autoimmune disorders. Yoga can aid in creating a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation, leading to better sleep quality. Gentle evening classes or practices focusing on calming postures may be particularly effective.
5. Cultivating Mind-Body Awareness
Yoga fosters a deeper connection between the mind and body. This heightened awareness can help individuals recognize their physical limits and understand their bodies' signals, allowing for better self-care.
6. Building Community
Practicing yoga in a group setting can provide social support, which can be beneficial for emotional health. Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can reduce feelings of isolation.
Incorporating yoga into your routine can create a supportive framework for managing symptoms associated with autoimmune disorders. By prioritizing mindfulness and gentle movement, yoga can contribute to enhanced well-being and a better quality of life.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) and asthma are both respiratory conditions that can impact lung function and overall well-being.
COPD is a progressive disease characterized by persistent airflow limitation, mainly caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, predominantly from cigarette smoke. Other contributors can include environmental pollutants and occupational exposures. COPD generally develops in adults over the age of 40 and may lead to serious complications, including respiratory infections, heart problems, and lung cancer. Management typically involves lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, along with medications like bronchodilators and corticosteroids to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory condition of the airways, often associated with allergic reactions and environmental factors. It can occur at any age and is characterized by episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing, particularly at night or early in the morning. Asthma symptoms can be intermittent, with periods of exacerbation followed by remission.
Practicing yoga can be beneficial for individuals with respiratory conditions by promoting improved lung function, enhancing respiratory efficiency, and reducing stress. Certain yoga poses and breathing techniques specifically target the respiratory system, helping to increase lung capacity and ease symptoms.
Integrating yoga into your routine can support respiratory health while fostering a sense of calm and well-being. Regular practice may lead to increased lung capacity, reduced symptoms, and a greater overall sense of control over your respiratory condition.
-
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), refers to a range of symptoms that continue for weeks or months after the initial COVID-19 infection has resolved. Individuals experiencing long COVID may endure various health challenges, including fatigue, shortness of breath, cognitive difficulties commonly referred to as "brain fog," joint pain, and persistent loss of taste or smell. The symptoms can fluctuate in intensity, making it a complex condition to identify and manage. Research is ongoing to understand the underlying mechanisms of long COVID, as well as to develop effective treatments. Current findings indicate that long COVID may affect multiple organ systems and could be linked to inflammation and immune dysregulation triggered by the virus.
Management of long COVID typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, addressing individual symptoms and improving overall quality of life. Integrating yoga into your recovery plan may provide additional benefits, helping to promote overall well-being and improve physical and mental health. While the journey through long COVID can be challenging, incorporating gentle yoga may help restore balance, reduce anxiety, and improve physical stamina. This mind-body practice can complement other recovery strategies, fostering a holistic approach to health and wellness.
-
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic illness that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective sheath, known as myelin, that covers nerve fibers. This damage disrupts communication between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to a variety of symptoms that can vary significantly from one person to another.
Common symptoms of MS include fatigue, numbness or tingling, difficulty walking, muscle weakness, vision problems, and cognitive challenges. The course of the disease can be unpredictable, with periods of relapses (worsening symptoms) and remissions (partial or complete recovery). Though the exact cause of MS remains unknown, genetic and environmental factors may play a role in its development. There is currently no cure for MS, but various treatment options are available to manage symptoms, slow the progression of the disease, and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle modifications, such as regular physical activity, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and adequate rest, are also important. For many individuals with MS, complementary approaches like yoga and mindfulness can provide significant benefits by enhancing overall well-being, promoting relaxation, and improving physical function.
Benefits of Yoga for MS
Improved Mobility: Yoga can help enhance flexibility and strength, which may aid in improving mobility and reducing stiffness.
Stress Reduction: The mindfulness aspect of yoga can decrease stress and anxiety, helping to alleviate some emotional symptoms associated with MS.
Pain Management: Gentle stretches and poses can help reduce muscle tension and chronic pain, promoting relaxation and comfort.
Balance and Coordination: Many yoga poses focus on stability, which may benefit individuals experiencing balance issues due to MS.
Enhanced Mind-Body Connection: Practicing yoga encourages a deeper awareness of the body and its sensations, which can foster a sense of control and empowerment.
Incorporating yoga into the lifestyle of individuals with multiple sclerosis can offer numerous benefits, from improving physical functions to enhancing mental wellness. A tailored approach that responds to individual capabilities and needs can foster a supportive environment for managing MS.
-
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is a condition that affects the autonomic nervous system, leading to an abnormal increase in heart rate when a person transitions from lying down to a standing position. This condition is classified under the broad category of dysautonomia, which involves dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions. Individuals with POTS often experience a rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness, dizziness, and even fainting when standing up. Other symptoms may include fatigue, palpitations, chest pain, nausea, and difficulty concentrating, often referred to as "brain fog." These symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, significantly impacting the affected person's quality of life. The exact cause of POTS remains unclear, but it is believed to involve several factors, including genetic predisposition, autoimmune disorders, or previous viral infections. POTS is more commonly diagnosed in women and often presents in adolescents and young adults.
Yoga can be a valuable tool for individuals with POTS to enhance their quality of life. Incorporating yoga can help manage these symptoms by promoting relaxation, improving circulation, and enhancing overall well-being. Gentle postures (asanas) that emphasize relaxation and grounding can help improve circulation without placing excessive strain on the body, and promote relaxation, which is beneficial for managing heart rate. Yoga practice also encourages deep relaxation and aids in stress reduction, which can alleviate some symptoms associated with POTS. The deep diaphragmatic breathing practices of Yoga help calm the nervous system and improve oxygenation, thereby supporting cardiovascular health. By focusing on gentle movements and mindful breathing, practitioners can work toward symptom management, increased relaxation, and overall well-being.
-
Musculoskeletal conditions encompass a wide range of disorders affecting the muscles, bones, and joints. These conditions can result from injuries, wear and tear, and various underlying health issues. Common examples include arthritis, osteoporosis, tendonitis, and back pain.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for individuals with musculoskeletal conditions, as it promotes flexibility, strength, and relaxation. When approached mindfully, yoga can help alleviate pain, improve function, and enhance overall well-being.
Key Benefits of Yoga for Musculoskeletal Conditions
Increased Flexibility: Many musculoskeletal conditions are characterized by stiffness and limited range of motion. Yoga poses stretch and lengthen muscles, which can increase flexibility and reduce discomfort.
Improved Strength: Specific yoga poses engage different muscle groups, helping to build strength. Strengthening the muscles around painful joints can provide better support and potentially alleviate pain.
Enhanced Posture: Yoga emphasizes body awareness and alignment. Correcting posture can reduce strain on muscles and joints, which is crucial for managing conditions like arthritis or chronic back pain.
Pain Management: Yoga incorporates mindfulness and breathing techniques, which can help manage pain perception and promote relaxation. This mental approach can make physical discomfort easier to cope with.
Stress Reduction: Living with a musculoskeletal condition can lead to emotional stress. Yoga encourages relaxation through mindfulness and deep breathing, helping to reduce anxiety and improve mood.
Yoga is not a substitute for medical treatment; however, it can be a valuable complementary practice for managing musculoskeletal conditions. By integrating yoga into your routine, you may find improvements not only in physical function but also in your overall quality of life.
-
Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) encompass a range of conditions characterized by increased joint flexibility and mobility that can lead to various symptoms and complications. Individuals with HSD may experience joint pain, fatigue, and a predisposition to injuries. These disorders exist on a continuum, from generalized joint hypermobility, where joints are more flexible than average, to hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (hEDS), which involves more severe manifestations and genetic components. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough clinical assessment, including the Beighton Score, which measures joint hypermobility.
Management of HSD is often multidisciplinary, focusing on symptom relief, enhancing joint stability, and improving overall function. An individualized approach to care can significantly impact quality of life, emphasizing the importance of tailored exercise programs, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, pain management strategies.
Yoga can be a valuable practice for individuals with hypermobility, focusing on stability, strength, and mindful movement to support joint health. Yoga for hypermobility disorders involves strengthening muscles around hypermobile joints and improving stability, as well as pain management and education on body mechanics and pacing strategies to help manage fatigue and prevent injuries. By focusing on controlled movements and awareness, individuals with hypermobility can enjoy the benefits of yoga while minimizing the risks associated with their unique body mechanics.
-
Osteoporosis and osteoarthritis are two distinct conditions that affect the skeletal system.
Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased fragility and a higher risk of fractures. This condition often develops silently over many years without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. Risk factors for osteoporosis include age, hormonal changes (particularly in postmenopausal women), a family history of the disease, inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. Preventive measures include maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in weight-bearing exercises, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol.
Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage protecting the ends of bones wears down over time. This condition leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the affected joints, most commonly in the knees, hips, hands, and spine. Osteoarthritis is influenced by factors such as age, obesity, joint injuries, repetitive stress on the joints, and genetics. Management strategies for osteoarthritis include physical therapy, weight management, pain relief medications, and lifestyle modifications that promote joint health.
While both conditions are related to aging and can significantly affect mobility and quality of life, they necessitate different approaches in terms of prevention, diagnosis, and management.
Yoga can be an effective practice for supporting bone health. Incorporating specific poses into your routine can enhance strength, balance, and flexibility, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones.
Benefits of Yoga for Bone Health
Weight-Bearing Exercise: Yoga poses that require you to lift your own body weight can stimulate bone growth and help increase bone density.
Improved Balance: Practicing balance poses can reduce the risk of falls, a significant factor in bone fractures, especially in older adults.
Increased Flexibility: Maintaining flexibility in your muscles and joints can reduce the risk of injuries and support skeletal alignment.
Enhanced Circulation: Yoga promotes better blood circulation, which can nourish bone tissue and promote overall health.
By integrating Yoga into your regular routine, you can cultivate a stronger foundation for your bones and overall well-being.
-
Depression is a complex mental health condition that encompasses a range of emotional, cognitive, and physical symptoms. It is often characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable. Individuals experiencing depression may also face challenges such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and feelings of worthlessness or guilt. These symptoms can vary significantly in intensity and duration, impacting daily functioning and overall well-being.
In navigating depression, it is important to recognize that support is available. Professional help from a therapist or counselor can offer valuable strategies to manage symptoms. Additionally, fostering a routine that includes self-care practices, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, mindfulness, and social connections, can be beneficial. Engaging in activities that promote mental well-being, such as yoga or meditation, can help create a sense of calm and provide tools for coping with stress.
Yoga can be an effective complementary practice for managing depression. It combines physical movement, breath control, and mindfulness, which can help enhance mood and promote emotional balance. Here are some ways yoga can support individuals experiencing depression:
1. Physical Movement
Engaging in yoga postures (asanas) encourages physical activity, which can release endorphins, natural mood lifters. Gentle movements, such as those found in restorative or yin yoga, help release tension and promote relaxation.
2. Breath Control
Pranayama, or breath work, is a core component of yoga that can reduce stress and anxiety. Techniques like deep breathing and alternate nostril breathing can help calm the nervous system, improve focus, and enhance overall well-being.
3. Mindfulness and Presence
Yoga encourages participants to focus on the present moment, fostering mindfulness. Practicing mindfulness can help individuals detach from negative thoughts and feelings associated with depression, allowing for greater emotional clarity and resilience.
4. Community and Support
Joining a yoga class offers the opportunity to connect with others, fostering a sense of community. Supportive environments can be beneficial for those dealing with depression, reducing feelings of isolation.
5. Structure and Routine
Incorporating regular yoga practice into one's schedule can provide a sense of routine and stability. This structure can be helpful for individuals struggling with depressive symptoms, as it encourages commitment to self-care.
While yoga is not a substitute for professional treatment, it can be a valuable addition to a comprehensive approach for managing depression. Consistent practice, combined with other therapeutic methods, may help individuals find greater balance and peace in their lives.
If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, reaching out to a mental health professional can be a crucial step toward recovery.
-
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by excessive fear or worry that can interfere with daily activities. Common types of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Individuals with anxiety disorders often experience symptoms such as restlessness, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and an overwhelming sense of dread. These symptoms may manifest in various situations, leading to avoidance behaviors that can further impact social interactions and personal relationships.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for individuals dealing with anxiety disorders. Combining physical postures, breath control, and mindfulness, yoga promotes relaxation and helps manage stress responses.
Benefits of Yoga for Anxiety
Stress Reduction: Yoga encourages a shift from the sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight response) to the parasympathetic nervous system (rest and digest). This shift can lead to reduced levels of cortisol, the stress hormone.
Mindfulness and Presence: Practicing yoga emphasizes being present in the moment, which can help individuals detach from worries about the past or future. Mindfulness practices incorporated in yoga can enhance self-awareness and provide tools to manage anxious thoughts.
Physical Outlet: The physical activity involved in yoga can release endorphins, enhancing mood and providing a sense of relief from anxiety. Gentle movements can also release tension built up in the muscles.
Breath Control: Pranayama, or breath control, is a key component of yoga. Focusing on the breath can aid in regulating emotions and promoting calmness, making it easier to handle anxiety.
Incorporating yoga into a routine can be a supportive practice for those managing anxiety disorders. While it can enhance overall well-being, it is essential to combine yoga with other therapeutic approaches as needed and consult with a healthcare professional when dealing with anxiety disorders.
It's important for those experiencing symptoms of anxiety to seek professional help. With appropriate support and treatment, individuals can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
-
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and trauma recovery represent significant areas of focus in the field of mental health. Those who experience trauma often face enduring effects that can manifest in various ways, including anxiety, depression, flashbacks, and emotional numbness. Understanding PTSD as a complex response to an overwhelming event is crucial in the recovery process.
Recovery from PTSD is not linear; it involves a multifaceted approach tailored to individual needs. Therapy options such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and exposure therapy are commonly used to help individuals process their trauma and develop coping strategies.
In addition to traditional therapy, integrating mind-body practices such as yoga can significantly contribute to recovery. Yoga fosters mindfulness, enhances body awareness, and helps individuals reconnect with their physical presence, which can be particularly beneficial for those who experience dissociation or bodily tension related to trauma. Breathwork is another powerful tool within trauma recovery. Focused breathing techniques can aid in regulating the nervous system, allowing individuals to manage anxiety and stress effectively. Grounding exercises that emphasize the present moment can also be beneficial, helping individuals to cultivate a sense of safety and stability.
Integrating yoga into trauma recovery can be a gentle yet powerful tool for healing, offering a pathway to regain a sense of safety, strength, and clarity.
Benefits of Yoga in Trauma Recovery
Grounding and Safety: Yoga encourages a deep connection to the body. Practices that focus on grounding, such as standing poses or seated postures, can help individuals feel more anchored and present.
Mindfulness and Awareness: Through mindful movement and breathwork, yoga fosters awareness of the body and emotions. This practice can facilitate the recognition and processing of trauma-related feelings without judgment.
Regulating Anxiety: Trauma often leads to heightened anxiety and stress responses. Techniques such as slow, intentional breathing and restorative poses help activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and calm.
Empowerment: Engaging in yoga allows individuals to reclaim their bodies and experience a sense of control. Choices in poses and the pace of practice can foster a sense of agency.
Community Connection: Group yoga sessions create a supportive environment where individuals can feel understood and validated in their experiences, helping to reduce feelings of isolation.
Yoga can serve as a complementary practice in trauma recovery, providing tools for self-regulation, mindfulness, and empowerment. It is essential to approach this journey with patience and compassion, allowing for gradual progress and honoring personal boundaries. Each individual’s experience is unique, and yoga can be adapted to meet those needs safely.
Ultimately, recovery from PTSD is a personal journey that requires patience and self-compassion. It is important for individuals to seek professional guidance and explore various therapeutic approaches to find what resonates best for them. By acknowledging their trauma and actively engaging in recovery practices, individuals can move toward healing and regain a sense of control over their lives.
-
Neurodiverse conditions encompass a wide range of neurological variations, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, and others. Each condition presents unique cognitive, behavioral, and sensory experiences that differ from neurotypical patterns. Individuals with neurodiverse conditions may experience heightened sensitivities to sensory input, challenges with social interactions, or differences in learning styles. This diversity in neurological functioning emphasizes the importance of creating inclusive environments that respect and accommodate varying needs. Understanding neurodiversity is essential for promoting acceptance and celebrating the differences that contribute to the richness of human experience. This approach encourages a shift away from a deficit-focused perspective toward one that values diversity and individuality.
Practices such as mindfulness and yoga can be beneficial for individuals with neurodiverse conditions. These practices promote self-awareness, emotional regulation, and relaxation, helping to manage anxiety and stress often associated with neurodiversity. Yoga, with its emphasis on mindfulness, breath control, and physical movement, can be a powerful tool for those navigating the complexities of neurodiversity. By adapting traditional yoga techniques, practitioners can find solace, self-regulation, and a deeper connection to their bodies and minds.
Additionally, the practice of yoga can foster self-awareness and emotional regulation, which are often areas of challenge for neurodiverse individuals. Through the exploration of breath work, meditation, and gentle movement, practitioners can develop strategies to manage stress, anxiety, and sensory overwhelm. Perhaps most importantly, yoga for neurodiversity emphasizes the importance of creating a safe, judgment-free space where individuals can explore their practice at their own pace. By cultivating an atmosphere of acceptance and understanding, yoga empowers neurodiverse practitioners to embrace their unique strengths and find solace in the practice. By recognizing and accommodating the diverse needs of practitioners, yoga is a transformative tool for personal growth, self-acceptance, and overall well-being.
-
Addiction is a complex condition characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli despite adverse consequences. It can affect individuals physically, mentally, and socially, leading to significant changes in behavior and lifestyle. Recovery from addiction is possible through various means, including therapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes. Approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) focus on changing thought patterns associated with addiction, while mindfulness practices can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies. Support systems play a vital role in recovery, providing a network of encouragement and understanding. Relapse is often a part of the journey, but it should be viewed not as a failure but as a necessary step towards growth and healing.
Addiction recovery is a complex journey that often requires a multifaceted approach to healing. Yoga can be a valuable tool in this process, offering physical, mental, and emotional benefits that support individuals in their recovery.
Benefits of Yoga in Recovery
Promotes Mindfulness: Yoga encourages present-moment awareness, helping individuals to cultivate mindfulness. This practice can reduce anxiety and cravings, enabling individuals to respond to triggers in a more balanced way.
Enhances Physical Health: The physical postures and breathing techniques in yoga can improve overall health, increasing strength, flexibility, and stamina. This can be particularly beneficial for those recovering from substance use, as it helps restore the body’s physical well-being.
Reduces Stress: Stress is a common trigger for relapse. Yoga helps activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing cortisol levels and promoting a sense of calm. This stress reduction can be crucial during recovery, as individuals learn to navigate challenging emotions without turning to substances.
Builds Emotional Resilience: Through regular practice, individuals can gain greater awareness of their emotions, learning to regulate feelings instead of avoiding them. This emotional resilience is essential for maintaining long-term recovery.
Fosters Community: Many recovery programs incorporate group yoga classes, providing a supportive environment where individuals can connect with others facing similar challenges. This sense of community can reduce feelings of isolation, which is often prevalent in addiction.
Integrating yoga into an addiction recovery journey can be deeply transformative. Its ability to cultivate mindfulness, enhance physical health, reduce stress, build emotional resilience, and foster community can empower individuals on their path to lasting recovery.
Ultimately, addressing addiction requires a holistic approach that considers the person's physical, emotional, and social well-being. By fostering an environment of compassion and support, individuals can navigate their path to recovery, embracing a healthier, more balanced life.
-
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting the necessary oxygen and nutrients. This disruption can result in the death of brain cells and lead to various neurological impairments, depending on the area of the brain affected. Long-term effects can range from mild to severe and may affect mobility, speech, cognitive function, and emotional health.
Preventive measures focus on managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and physical inactivity. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle—incorporating balanced nutrition, exercise, and stress management—can significantly reduce the likelihood of a stroke.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for individuals recovering from a stroke, helping to improve physical strength, flexibility, balance, and mental well-being.
Gentle movements and restorative poses can help to improve circulation and reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation without placing excessive strain on the body, while engaging in deep, mindful breathing can reduce anxiety and enhance focus. Poses that challenge balance can aid in coordination and stability, and assist in gradually building strength and confidence, while gentle stretching can help restore flexibility in muscles and joints, while minimizing discomfort. Furthermore, cultivating a connection between the mind and body through Yoga practice supports emotional healing and fosters resilience.
Yoga offers a holistic approach to stroke recovery by enhancing physical strength, promoting relaxation, and improving overall mental health. With proper guidance and a mindful attitude, integrating yoga into your recovery can be a meaningful step toward regaining function and well-being.
-
Post-surgical recovery is a delicate time for the body, requiring a gentle approach to movement and healing. Yoga can serve as an effective tool to promote recovery, improve mobility, and foster relaxation.
Yogic breathing practices can enhance relaxation, reduce stress, and increase oxygen flow to healing tissues. Restorative and gentle postures help the body to gradually ease back into movement, and allow for deep relaxation without exertion. Mindfulness practices such as meditation and visualization foster a positive outlook during your healing journey, and support your mental and emotional well-being - which is just as crucial as physical recovery.
Yoga can be a wonderful companion in your post-surgical recovery, offering a gentle pathway to regain strength, flexibility, and tranquility. Always prioritize self-care and seek guidance from professionals to ensure a safe and effective practice.
Before starting any yoga practice post-surgery, consult with your surgeon or healthcare provider. They can provide specific guidelines based on your individual situation and surgical procedure.
-
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can lead to age-related conditions, including arthritis, cognitive decline, osteoporosis, and vision and hearing loss. Awareness and proactive management of age-related conditions can lead to healthier and more fulfilling years. Prioritizing health and well-being through lifestyle choices and regular check-ups is key to navigating the aging process effectively.
Yoga can be a beneficial practice for individuals as they age, promoting physical, mental, and emotional well-being. The gentle nature of yoga makes it accessible and adaptable for different fitness levels, which is particularly advantageous for older adults.
Benefits of Yoga for Aging:
Improved Flexibility: Regular yoga practice helps maintain and enhance flexibility, which can diminish with age. Poses like the cat-cow stretch or seated forward bend can safely increase range of motion in the joints.
Enhanced Balance: Balance poses such as tree pose or warrior III can help improve stability, reducing the risk of falls—a common concern for aging individuals.
Strength Building: Many yoga poses engage various muscle groups, promoting strength. Poses like chair pose or downward-facing dog can be modified to support strengthening without straining.
Stress Reduction: Yoga incorporates mindfulness and breathing techniques that can reduce stress and anxiety. Practices such as gentle restorative yoga or yoga nidra can encourage relaxation and a sense of peace.
Better Posture: As we age, maintaining proper posture can become more challenging. Yoga helps to develop body awareness, which can promote better alignment and posture over time.
Enhanced Circulation: Specific poses can boost circulation, benefiting overall heart health and supporting various systems within the body.
Mindfulness and Mental Clarity: The meditative aspects of yoga promote mindfulness, enhancing mental clarity and cognitive function. This can be especially valuable as we age, helping to combat challenges related to memory and focus.
Pain Management: Regular yoga practice can alleviate pain associated with arthritis, joint issues, and chronic conditions. Gentle movements combined with breathwork can ease discomfort and lead to improved mobility.
Incorporating yoga into a regular routine can promote a holistic approach to aging, supporting physical health, emotional resilience, and overall quality of life.
Expert Care Customized to You + Your Unique Healing Journey.
Because Yoga Therapy is personalized to meet the specific needs, goals, and desired outcomes of the individual, treatment duration may vary from short-term support (over the course of several weeks) to providing more long-term management (lasting months or years). The course and duration of treatment depends entirely on the individual patient, their condition(s), and their desired goals and outcomes.
This unique, holistic approach to healing and whole-person healthcare ensures that no Yoga Therapy treatment or session is ever the same. Each session is a dynamic collaboration between Yoga Therapist and client, affording a greater degree of flexibility, responsiveness, and adaptability than many other approaches to health and wellness may allow, ensuring the Yoga Therapist is better able to meet the needs of the individual just as they are.
Yoga Therapy is inclusive, accessible, adaptable, and customizable. It respects individual differences in age, culture, religion, philosophy, occupation, and mental and physical health, and is applied with great care and intention to best meet the patient where they are, as they are, throughout their unique healing journey.
Client Testimonials
“Colure came into my life at just the right moment. I was still struggling emotionally with the loss of my much loved husband, and a very good friend and fellow yoga enthusiast was working with Colure. This good friend and I share the same primary care physician, who had recommended Colure to her. Colure’s focus on therapeutic and restorative yoga was exactly what I needed. I found my twice weekly private sessions in my home with her both mentally and physically soothing and strengthening. In addition to her excellence as a yoga therapist, Colure is also a wonderfully kind and thoughtful person. It was always a pleasure to work with her."
~ Rita Lowndes, Winter Park FL
"Having Colure as a Yoga Therapist was one of the best decisions I ever made. I was hoping to find relief from my back pain; Not only was my pain was relieved; I started to regain my flexibility, and it felt like years of bad habits were undone. It was great to have someone who became knowledgeable about me and tailored a plan accordingly. I am grateful for everything I learned, and would happily do it over again!"
~ Anthony Gilardi, Oviedo FL
"I had the privilege of practicing yoga with Colure for several years, twice a week in my home. Her extensive knowledge of physiology and how the body works is amazing. Whether I was working on bursitis in my hip, plantar fasciitis, or just a crick in my neck she came up with the perfect practice. And she always kept it interesting— no two practices were ever the same. I would highly recommend her to anyone looking for a yoga therapist who not only knows her business well, but is a genuinely lovely person."
~ Alexis Pugh, Winter Park FL
Book a Free Consultation!
Curious to learn more about how Yoga Therapy can help you? Book a Free
30-minute Exploratory Call, and find out!
We specialize in working with individuals like you to address specific health needs & wellness goals by developing personalized tools & practices that meet you where you are.
During your 30-minute session, you’ll review your health history, discussing any challenges or symptoms you are currently experiencing, outline your Yoga Therapy goals, and learn all about how we work with you to co-create a personalized treatment plan that will start moving you forward in the direction you desire.






